As you become more familiar with the LCSC ColorEasyDuino development board, you will find it easier to face potential problems. These FAQs help you overcome obstacles from hardware to software. Remember, every problem has a solution, and learning and practice are the keys to success. We hope these FAQs have been a valuable aid in your electronic projects. We wish you a journey in electronic innovation that goes further and further, continuously creating new possibilities.
The Development Board Is Not Recognized
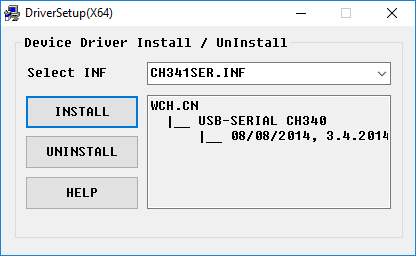
The development board is based on the USB serial port converter CH340 for downloading programs and communication. If it is not recognized successfully, it indicates that the CH340 driver has not been correctly installed.
Driver download address:
https://www.wch-ic.com/downloads/CH341SER_EXE.html
After downloading, you can directly install it.
Common IDE Error Issues
“avrdude: stk500_getsync(): not in sync: resp=0x00”.
sync: resp = 0x00 is a generic response, which means that the “Atmega chip” on the Arduino development board is not working. When this happens, there are many possible errors:
- Ensure that there are no connections on digital pins 0 and 1 of the Arduino (including expansion boards)
- Ensure that the correct COM port and development board are selected in the Tools menu
- Press the reset button on the Arduino several times, then upload the code again
- Disconnect and reconnect the Arduino to the PC
- Restart the Arduino IDE
- The bootloader of the development board has a problem and needs to program the Arduino firmware
Invalid device signature

When uploading code to the development board, an error occurs. This is because the correct development board is not selected in the IDE. Since the device signature on the development board is different from the one selected in the IDE, this error usually occurs. The correct one should be selected as shown in the following figure:

LCSC ColorEasyDuino is a development board that is compatible with the Arduino ecosystem. It has a variety of peripheral interfaces that include UART, I2C, SPI, ADC, and PWM.
Related Articles:
