Selective soldering allows for precise operations on specific solder joints, avoiding any impact on surrounding components, thereby enhancing both production efficiency and product quality. As electronic devices become increasingly complex and miniaturized, selective soldering technology is widely applied in industries such as industrial control, consumer electronics, and automotive electronics.
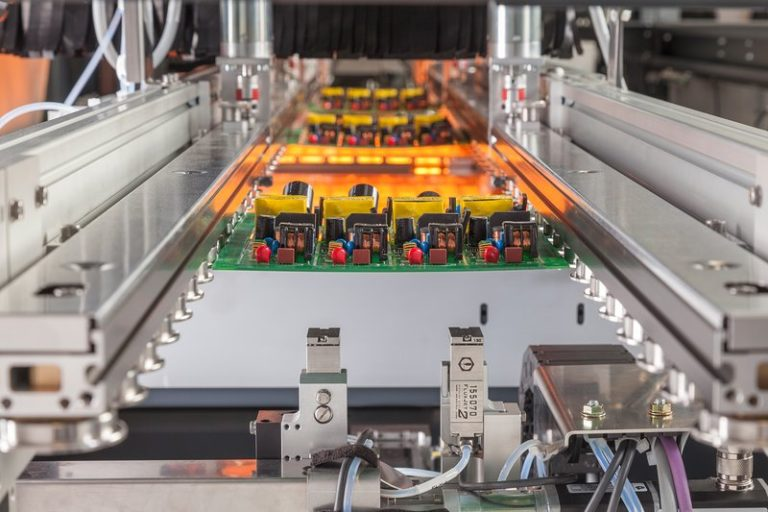
Industrial Control: Meeting the Demands of Complex Circuits
Industrial control systems are highly automated and complex devices that require a high level of reliability and stability in their circuit boards. Selective soldering effectively meets these needs, especially when dealing with multi-layer PCBs and complex circuit layouts. Traditional methods may fail to meet these high-precision, high-density requirements, while selective soldering ensures the quality and consistency of each solder joint through precise positioning and automated control.
Applications:
- High-Precision Soldering of Multi-Layer PCBs: Industrial control devices often require multi-layer circuit boards with very tight spacing between circuits. Traditional methods struggle to guarantee the stability of each solder joint. Selective soldering can accurately control the soldering position, avoiding defects or short circuits.
- Mixed Assembly Requirements: Industrial automation equipment often involves a mix of through-hole components and surface-mount components, which presents higher soldering requirement. Selective soldering can precisely handle different types of components, ensuring the quality of connections between all parts. Common applications include power management systems, automation controllers, and communication devices.
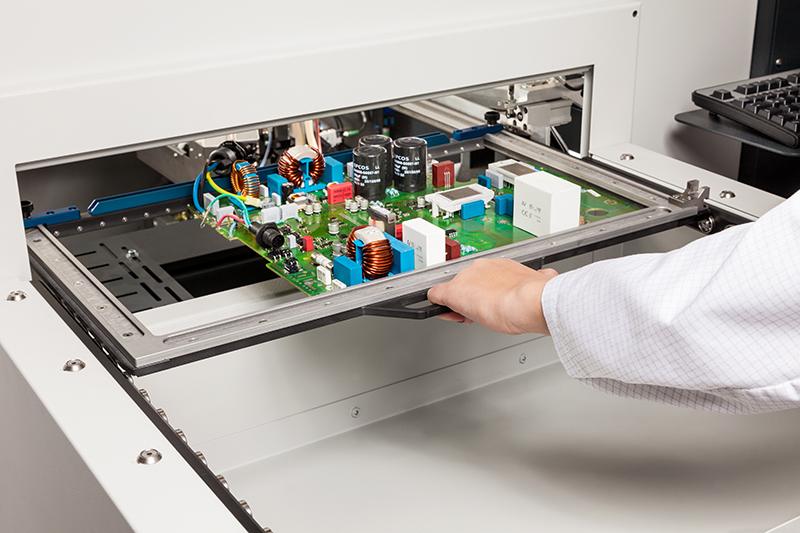

Selective Soldering process (Image source: online)
Technical Advantages:
- High Reliability: Selective soldering ensures a high-reliability environment with advanced nitrogen protection to prevent oxidation and solder joint defects, thereby improving the overall reliability of the circuit board.
- Efficiency: Compared to hand soldering, selective soldering significantly increases production efficiency and reduces errors and rework time.
Consumer Electronics: Advantages of Miniaturization and Integrated Circuits
The development trend in the consumer electronics industry features in lighter, thinner designs, more integrated, and high-performance. This creates immense challenges for circuit board design and soldering techniques. With the widespread use of miniaturized products such as smartphones and wearable devices, selective soldering has become the ideal choice for manufacturing these products.
Applications:
- High-Precision Soldering: Many components in consumer electronics are very small, often featuring complex geometries and tight spacing. Selective soldering can complete the soldering task with high precision without affecting other components, fulfilling the production requirements for miniature components.
- Complex Assembly Structures: As the integration of electronic products increases, the assembly structure on circuit boards becomes more complex. Selective soldering can adapt to various complex assembly structures through flexible nozzle designs, ensuring each solder joint is completed precisely.
Technical Advantages:
- High-Density Soldering: In space-constrained multi-layer PCBs, selective soldering meets the demand for high-density demand, ensuring the quality of solder joints and the reliability of circuits.
- Stability: Due to the precision of selective soldering, it effectively reduces unstable factors in the soldering process, enhancing long-term stability of the product.
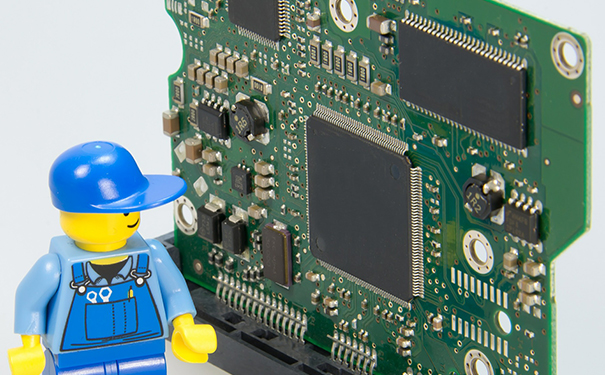
Printed circuit board with SMD components on (Image source: online)
Automotive Electronics: Demand of Reliability Soldering Technology
With the rapid development of smart and electric vehicles, automotive electronic systems are becoming increasingly complex. These systems not only need to meet high safety and reliability standards but must also operate stably in harsh working environments. Selective soldering has proven advantageous in automotive electronics, particularly for high-precision and high-reliability soldering.
Applications:
- Soldering of Complex Modules: Automotive electronic systems include navigation systems, sensors, and ECUs (electronic control units), all of which require high-quality soldering. Selective soldering ensures the reliability of each solder joint, especially in environments with significant temperature fluctuations and vibration, where joint stability is critical.
- Climate Resistance: Automotive electronics must function in extreme environments, and the nitrogen-protected soldering environment in selective soldering prevents oxidation, enhancing the solder joint’s durability.
Technical Advantages:
- Oxidation Resistance: The nitrogen protection during selective soldering prevents oxidation, ensuring that solder joints remain stable and reliable in high-temperature, high-humidity, and prolonged-use environments.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Improved soldering quality results in significantly lower maintenance costs for automotive electronic systems, reducing failure rates and extending the vehicle’s lifespan.
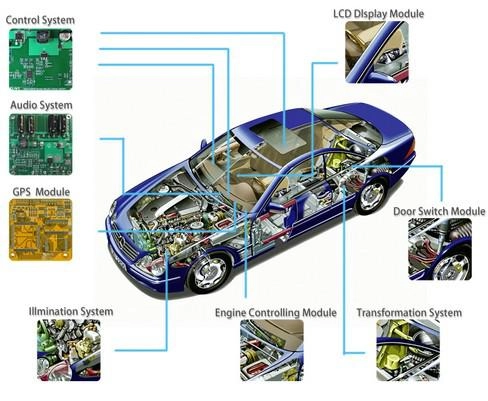
Applications for Automotive (Image source: online)
Medical Equipment: Quality and Safety
Medical devices have stringent requirements for the quality and cleanliness of their electronic components because soldering defects can significantly impact device performance and patient safety. Selective soldering plays a crucial role in manufacturing medical devices, particularly in meeting high precision and cleanliness standards.
Applications:
- High-Cleanliness Soldering: Medical devices require high cleanliness standards and contamination-free environments. Selective soldering uses enclosed environments and precisely controlled soldering processes to ensure each solder joint is completed in a clean environment. This approach avoids any soldering defects that could lead to functional failures or device malfunctions, ensuring stable and long-lasting operation.
- Precise Temperature Control: Electronic components in medical devices are often sensitive to temperature. The preheating module in selective soldering precisely controls temperature fluctuations to avoid damage to sensitive components, ensuring the safety and stability of the components.
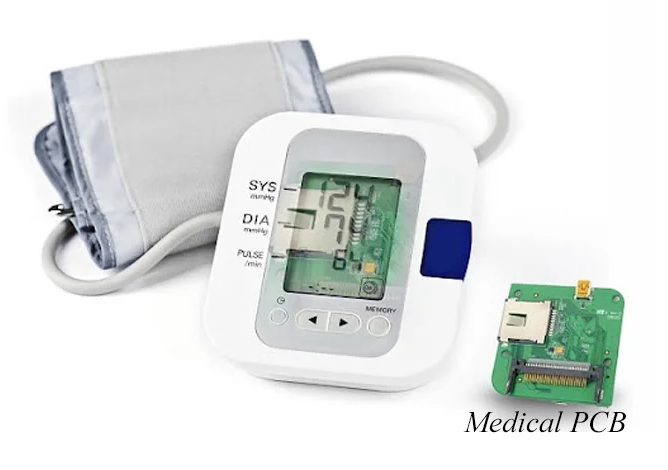
Medical device and its PCB (Image source: online)
Technical Advantages:
- Anti-oxidation Environment: Selective soldering uses inert gases like nitrogen to protect the soldering process, preventing the formation of oxides and ensuring the purity of the solder joint, which reduces the long-term impact on the device’s performance.
- Precise Temperature Control: Through precise temperature control, selective soldering ensures that temperature fluctuations during the soldering process do not damage sensitive components, ensuring the safety and reliability of medical equipment.
Selective soldering provides significant advantages across multiple sectors, including industrial control, consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and medical devices. It dramatically boosts production efficiency and ensures superior product quality and long-term stability.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
Previous: How Selective Soldering Reduces PCB Defects and Improves Reliability
Custom Cables: Save 50%+ Avg Cost By JST, Molex, TE Alternatives | Processing Fee Down to $1 Per Piece | No Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) Required
PCB & PCBA: New Customer Get Coupons Up to $125 | 1 – 32 Layers From $2 /5pcs | PCB Assembly From $8 /5pcs
Front Panels: High-quality Front Panel Acylic/PET | Front Panel Order Up to 30% Off | Membrane Switch Available Soon
