An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is an embedded system within automotive electronics that manages one or more electrical systems or subsystems in a vehicle. Modern vehicles often contain numerous ECUs dedicated to specific functions to enhance performance, safety, and user experience.
Main Components and Working Principles of an ECU
The operation of an ECU can be summarized as a closed-loop control process: “input → processing → output.” Its core function is to adjust the vehicle system status in real time through the coordinated work of sensors, algorithms, and actuators. The main components of an ECU include:
- Microcontroller:
Acts as the brain of the ECU, processing inputs from sensors and executing control algorithms.
- Memory:
Stores software programs and data, including calibration tables and fault codes.
- Input Interfaces:
Receive signals from various sensors monitoring parameters like temperature, pressure, and speed.
- Output Drivers:
Send commands to actuators such as fuel injectors, ignition coils, and motors to perform specific actions.
- Communication Interfaces:
Enable the ECU to communicate with each other over in-vehicle networks like the Controller Area Network (CAN) or Ethernet.
The ECU operates by receiving real-time data from sensors throughout the vehicle that monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and oxygen levels. The ECU processes this information using pre-programmed instructions and algorithms, then sends commands to actuators—such as adjusting fuel injection or activating the cooling fan—to optimize system performance. Throughout this process, the ECU continuously monitors sensor feedback and dynamically adjusts its outputs in real time to maintain precise and adaptive control of the vehicle.
Primary Functions of the Electronic Control Unit
Modern ECUs manage various features, including:
- Engine Management:
The Engine Control Module (ECM) regulates critical engine operations such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and idle speed control. By processing data from various sensors—like the mass air flow sensor, throttle position sensor, and oxygen sensors—the ECM ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
- Transmission Control:
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) oversees gear shifting in automatic transmissions, adjusting shift points for smooth operation and fuel economy.
- Braking Systems:
Brake Control Modules (BCM or EBCM) manage systems like Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC), enhancing vehicle safety during braking and cornering.
- Body Controls:
Body Control Modules (BCM) handle various functions such as power windows, door locks, interior lighting, and climate control, contributing to passenger comfort and convenience.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS):
Certain ECUs are dedicated to ADAS features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automated parking, enhancing driver safety and comfort.
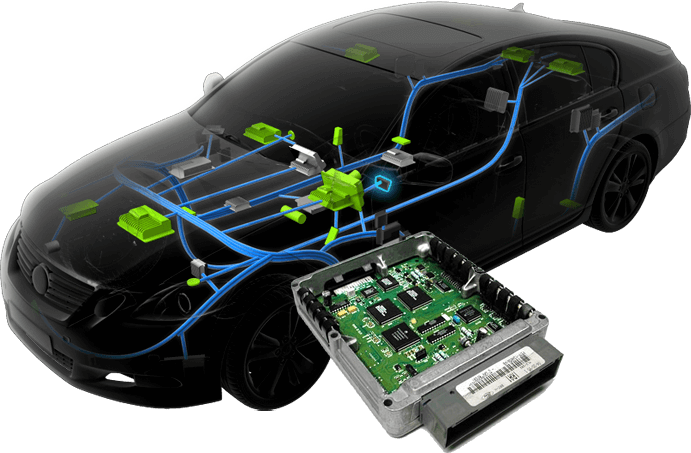
In summary, the ECU serves as the central processing unit of vehicles’ engine management system, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and compliance with emission standards through continuous monitoring and control of engine functions.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
Custom Cables: Save 50%+ Avg Cost By JST, Molex Alternatives | Processing Fee Down to $1/pcs | No Minimum Required
PCB & PCBA: New Customer Get Coupons Up to $105 | 1 – 32 Layers From $2/5pcs | PCB Assembly From $8/5pcs
Front Panels: High-quality Front Panel Acrylic/PET | Front Panel Order Up to 30% Off | Membrane Switch Available Soon
