What is an RF antenna? This week, LCSC supplier BAT WIRELESS introduced the function and status of RF antennas in wireless communication.
Internet of Things communication is one of the most active and rapidly developing fields in today’s communications field. The RF antenna serves as a communication bridge between the user’s terminal and the control equipment of the communication base station. They find applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) communications and wireless access communication systems. Its rapid development has generated a significant impetus, driving transformation in antenna concepts and technological innovation.
RF Antenna Principle :
RF antennas play a pivotal role as the link between user terminals and communication base station equipment. Radio waves, which are central to this process, are electromagnetic and propagate with a speed related to their medium, peaking at the speed of light in a vacuum.To understand the principle of RF Antenna, you need to know the basics of radio waves.
Radio waves are a form of energy transmission. During the propagation process, the electric field and magnetic field are perpendicular to each other in space, and both are perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
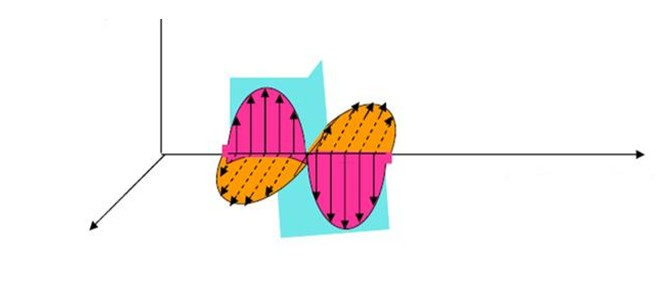
Radio waves, like light, have a propagation speed related to the propagation medium. Radio waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, represented by C=300000 kilometers/s. The propagation speed in the medium is V=C/(e)~1/2, where e is the relative dielectric constant of the propagation medium.
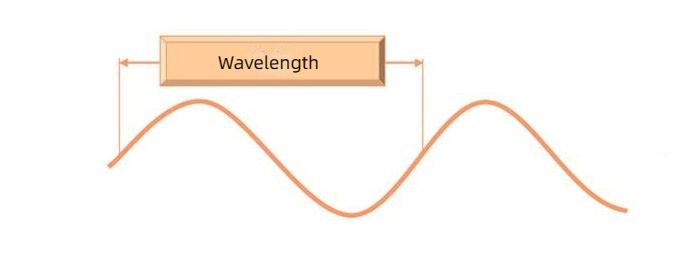
The relationship between wavelength, frequency and propagation speed of radio waves: It can be expressed by U=V/F. In the formula, V is the speed in m/s; U is the wavelength in m; F is the frequency in Hz. When radio waves of the same frequency propagate in different media, the speed is different, so the wavelengths are also different.
RF Antenna Function and Status:
The radio frequency (RF) signal power that outputs from the radio transmitter travels through the feedline (cable) to the antenna. Then, the antenna radiates it out in the form of electromagnetic waves. After the electromagnetic waves reach the receiving location, they are received by the antenna and sent to the wireless receiver through the feeder. The antenna is an essential radio equipment that transmits and receives electromagnetic waves. Without the antenna, there would be no wireless communication.
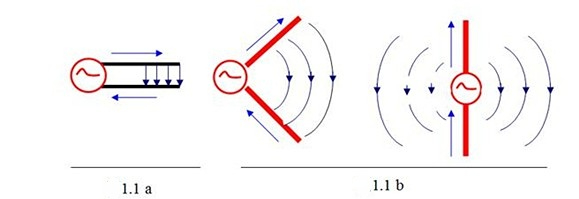
There are numerous types of antennas. We can categorize them based on their applications and frequency bands.
- According to their uses: communication antennas, TV antennas, radar antennas, etc.
- According to the working frequency band: shortwave antenna, ultra-shortwave antenna, and microwave antenna.
The working frequency bands of the antenna are as follows: 315MHZ, 433MHZ, 470MHZ, 868MHZ, 915MHZ, 2.4G, 5.GHZ, 5.8GHZ.
Communication industry frequency: 700-2800MHZ (GSM, GPRS, CDMA, 2G, 3G, 4G)
- Divided according to directionality: omnidirectional antenna and directional antenna
- According to the appearance: linear antenna and planar antenna.
- According to the material: AP (glue stick) antenna, FPC soft board antenna, Rigid PCB antenna, spring antenna, copper tube antenna, ceramic antenna, metal antenna, fiberglass antenna, etc.
Related Articles:
Understanding 5G Antenna Requirements – Electronic Components Distributor – LCSC Electronics
