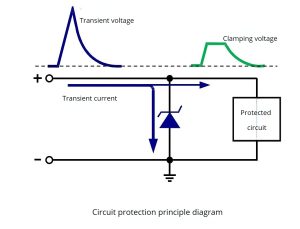
A transient voltage suppressor diode (TVS) is also an avalanche breakdown diode. It is a new product developed based on the voltage regulator tube technology. Its circuit symbol and its appearance are the same as an ordinary diode. There are unidirectional and bidirectional transient voltage Suppressors. A unidirectional transient voltage suppressor serves in DC circuits, and bidirectional TVS serves in AC circuits. The transient voltage suppressor is connected in reverse parallel in the circuit. When the circuit is working, it is in a cut-off state (high impedance state) and does not affect the operation of the circuit. When an abnormal overvoltage occurs in a circuit and reaches its (avalanche) breakdown voltage, it quickly changes from a high resistance state to a low resistance state, discharges the instantaneous overcurrent caused by the abnormal overvoltage to the ground, and at the same time clamps the abnormal overvoltage behind it. Within the safe level that the secondary circuit can withstand, thereby protecting the subsequent circuit from damage by abnormal overvoltage. When the abnormal overvoltage disappears, the transient voltage suppressor resistance returns to the high resistance state.
Transient Voltage Suppressor Selection Guide
When selecting a Transient Voltage Suppressor, we consider the following factors:
(1) If the transient Voltage Suppressor is likely to withstand the impact of peak pulse voltages (surge voltage) from two directions, we select bipolar ones. Otherwise, we select unipolar ones.
(2) The Vc value of the selected transient Voltage Suppressor should be lower than the maximum voltage of the protected component. Vc is the voltage of the diode in the cut-off state, which is the voltage passing through the transient Voltage Suppressor during ESD impact. It cannot be greater than the tolerable limit voltage of the protected circuit. Otherwise, the device is in danger of being damaged.
(3) Transient Voltage Suppressor should not be in a breakdown state under normal working conditions. It is best to be below VR. We should consider the requirements of VR and VC when selecting the appropriate transient Voltage Suppressor.
(4) If you know the more accurate surge current IPP, you can use VCIpp to determine the power; if you are unsure of the approximate range of IPP, it is better to choose a transient Voltage Suppressor with higher power. The PM is the maximum peak pulse power dissipation that a transient Voltage Suppressor can withstand. Under a given maximum clamping voltage, the greater the power consumption PM, the greater its surge current tolerance; under a fixed power consumption PM, the lower the clamping voltage VC, the greater its surge current tolerance. In addition, the peak pulse power consumption is also relevant to the pulse waveform, duration, and ambient temperature.
(5) The transient pulses that the transient Voltage Suppressor can withstand are non-repetitive, and the pulse repetition frequency (ratio of duration and intermittent time) specified by the device is 0.01%. If repetitive pulses appear in the circuit, we should consider the accumulation of pulse power. Otherwise, it may damage the transient Voltage Suppressor.
(6) You can consciously add a current-limiting resistor to the line to protect small current loads. It will generally not affect the operation of the line as long as the resistance of the current-limiting resistor is appropriate. It will reduce the current interfered with by the current-limiting resistor. However, it is possible to use transient Voltage Suppressor tubes with lower peak power to protect small current load lines.
(7) The junction cross-section of the Voltage Suppressor avalanche determines the capacitance C measured at a specific frequency of 1 MHz. The size of C is proportional to the current carrying capacity of the transient Voltage Suppressor. If C is too large, the signal will attenuate. Therefore, C is a primary parameter for selecting a transient Voltage Suppressor for data interface circuits. For loops with higher data/signal frequencies, the more the diode capacitance interferes with the circuit, the more noise or attenuation the signal strength is. Therefore, the capacitance range of the selected device needs to be determined based on the characteristics of the loop. Generally, the high-frequency circuits should choose capacitance as small as possible (such as LCTVS and low-capacitance TVS, the capacitance is no more than 3 pF). For Circuits with low capacitance requirements, the capacitance of the capacitor can be higher than 40 pF.
(8) To meet the IEC61000-4-2 international standard, TVS diodes must be able to handle a minimum ESD impact of 8 kV (contact) and 15 kV (air). Some semiconductor manufacturers use higher impact resistance standards in their products. Designers can select devices for portable device applications with special requirements as needed.
Transient Voltage Suppressors Model Recommendation
Transient voltage suppressordiode SMAJ series:
SMAJ5.0CA, SMAJ15CA, SMAJ36CA, SMAJ440A, SMAJ440CA;

Transient voltage suppressordiode SMF series:
SMF33CA, SMF36CA, SMF36A, SMF5.0CA, SMF10CA;

Transient voltage suppressordiode SMBJ series:
SMBJ5.0CA, SMBJ6.5CA, SMBJ8.0CA, SMBJ15CA, SMBJ22CA, SMBJ24CA, SMBJ26CA, SMBJ30CA, SMBJ36CA, SMBJ440CA;

Transient voltage suppressordiode SMCJ series:
SMCJ18A, SMCJ24A, SMCJ24CA, SMCJ30CA, SMCJ33CA, SMCJ33A, SMCJ36A, SMCJ36CA, SMCJ48A, SMCJ48CA, SMCJ58A, SMCJ64CA;

Transient voltage suppressorautomotive grade series:
SM8S10A, SM8S12A, SM8S13A, SM8S14A,

MDD Brand Transient Voltage Suppressor Features
⑴ The internal chip of TVS is made of semiconductor silicon material and uses semiconductor technology, which has high reliability.
⑵ Transient Voltage Suppressor has low dynamic internal resistance and low clamping voltage.
⑶ Transient Voltage Suppressor has a faster response speed than other overvoltage protection devices.
⑷ Transient Voltage Suppressor voltage has high accuracy, generally ±5% deviation. In special applications, higher accuracy can be achieved through process improvement or parameter screening.
⑸ TVS packaging is diverse, and chip packaging includes SOD-123, SMA (DO-214AC), SMB (DO-214AA), SMC (DO-214AB), etc.
⑹ The transient power of TVS can reach 200W~30KW under the 10/1000μs waveform, or even higher. Under the 8/20μs waveform, the transient peak pulse current can reach 3KA, 6KA, 10KA, 16KA, 20KA, or even higher.
⑺ The working voltage range can be from 5V to 600V or even higher.
About MDD
Shenzhen Chendaxing Electronics Co., Ltd. (MDD) was established in 2008. It is a national high-tech enterprise specializing in the research, development, and production of semiconductor discrete devices.
Through continuous efforts, the high-quality “MDD” brand has won the trust and support of our customers. The company invested in building a packaging factory in Changzhou, Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu Chendaxing Electronics Co., Ltd. covers an area of 24 acres, with a construction area of 15,000 square meters, and currently has 300 employees. There are more than 600 people, and the total annual production and sales of diodes and rectifier bridges is about 6 billion.
The factory has introduced a full set of foreign advanced equipment and scientific management system, with SOD-123, SOD-123FL, SOD-323, SMA, SMAF, SMB, SMBF, SMC, TO-277, TO-252, TO-220, UMB, MBS, MBF, ABS, KBP, GBU, GBJ, KBPC, R-1, DO-41, DO-15, DO-201AD, R-6, SOT-23, SOT-89, SOD-523, DFN and other packaging forms Diode/rectifier bridge production line; complete varieties and specifications, including ordinary rectifier, fast recovery, high efficiency, ultra-fast, Schottky, rectifier bridge, as well as bidirectional trigger, high voltage, Transient Voltage Suppressor, switching, voltage stabilization and other series Diode/Bridge Rectifier.
LCSC electronics is the authorized distributor of MDD. Select MDD’s products at LCSC electronics.
